Hot work: fire risk and prevention
Hot work processes are those activities and operations that involve the use of open flames or the generation of heat that can easily cause fires if not handled properly. Examples of common hot work are welding, cutting, forging and melting of metals, thermodrilling of plastics, hot asphalt work, industrial drying operations.

The Confederation of Fire Protection Associations Europe (CFPA-Europe) is an association of national organisations in Europe concerned primarily with fire prevention & protection and also safety & security and other associated risks. It was founded in 1974 and in the guideline “fire safety basics for hot work operatives” CFPA-E Guideline No 12:2023 Fit provides the main guidelines to be followed and kept in mind for safety at work in hot work.
Risk assessment
The main risks associated with hot work include fire, burns and exposure to harmful substances. It is therefore essential to identify and classify possible hazards so that appropriate preventive and protective measures can be taken. In order to correctly identify the risks in hot work, a careful analysis of the environmental conditions is useful, evaluating the presence of flammable materials, the ventilation of the work area and the possibility of spreading fires.
Once potential risks have been identified, operational procedures can be established and activities planned. It is also important to provide the personnel involved with specific training regarding the safety measures to be taken in the event of an emergency and the correct use of personal protective equipment.
Hot work PPE
Among the most common PPE used for this type of work are heat insulating gloves, which protect hands from high heat and burns. It is crucial that the gloves are quality and adequately sized to ensure effective protection. It is also advisable to use fireproof overalls or heat-insulating jackets, which protect the body from the risks of burns, and non-slip and puncture-proof footwear.
Another important PPE for hot work is the face masks with a gas and vapour filter, which protect the respiratory tract from harmful agents emitted during welding or thermal cutting. To protect the eyes from splashing molten metal during welding, there are transparent face shields or specific anti-uv and infrared goggles.
Safety precautions and training
Before starting any hot work you must ensure that all personnel involved is properly trained and aware of the risks associated with hot work. It is important to wear appropriate personal protective clothing and equipment, such as sweat suits, heat insulating gloves, non-slip shoes and goggles. Before starting any operation, it is essential to carefully check that the instruments and equipment are in good condition and that they have been subjected to the necessary inspections and maintenance.
During hot work, it is essential to maintain adequate ventilation at the workplace to prevent the accumulation of harmful gases or toxic vapours. It is also important to keep the temperature of the tools and hot surfaces under control to prevent burns or accidental fires. All workers involved must be aware of the emergency procedures to be followed in an emergency.
Hot work permit
To ensure a safe working environment during hot work operations, safe temperature limits must be established to prevent overheating of equipment and to prevent fire. In addition, it is important to maintain adequate ventilation in the areas where hot operations will be carried out to prevent the accumulation of toxic gases or harmful vapours. The hot work permit is the work permit itself which should be issued only after assessing the risks and having taken all necessary safety measures.
Below is an excerpt from the hot work permit form from the CFPA-E Guideline No 12:2023 F.
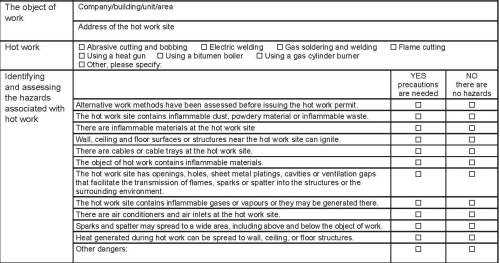
During the authorisation process, it is also important to take into account the level of experience and training of the workers involved, making sure that they are able to safely handle hot operations. During hot work operations, it is essential to strictly comply with all established safety procedures, avoiding negligent or non-compliant behavior. In case of emergency during hot operations, all workers must be able to act promptly according to established safety protocols. Finally, it is important to conduct regular inspections of equipment used during hot operations to ensure compliance and proper operation.
